- Why Use Binary Trees?
- Tree Terminology
- An Analogy
- How Do Binary Search Trees Work?
- Finding a Node
- Inserting a Node
- Traversing the Tree
- Finding Minimum and Maximum Key Values
- Deleting a Node
- The Efficiency of Binary Search Trees
- Trees Represented as Arrays
- Printing Trees
- Duplicate Keys
- The BinarySearchTreeTester.py Program
- The Huffman Code
- Summary
- Questions
- Experiments
- Programming Projects
Finding a Node
Finding a node with a specific key is the simplest of the major tree operations. It’s also the most important because it is essential to the binary search tree’s purpose.
The Visualization tool shows only the key for each node and a color for its data. Keep in mind that the purpose of the data structure is to store a collection of records, not just the key or a simple color. The keys can be more than simple integers; any data type that can be ordered could be used. The Visualization and examples shown here use integers for brevity. After a node is discovered by its key, it’s the data that’s returned to the caller, not the node itself.
Using the Visualization Tool to Find a Node
Look at the Visualization tool and pick a node, preferably one near the bottom of the tree (as far from the root as possible). The number shown in this node is its key value. We’re going to demonstrate how the Visualization tool finds the node, given the key value.
For purposes of this discussion, we choose to find the node holding the item with key value 50, as shown in Figure 8-8. Of course, when you run the Visualization tool, you may get a different tree and may need to pick a different key value.
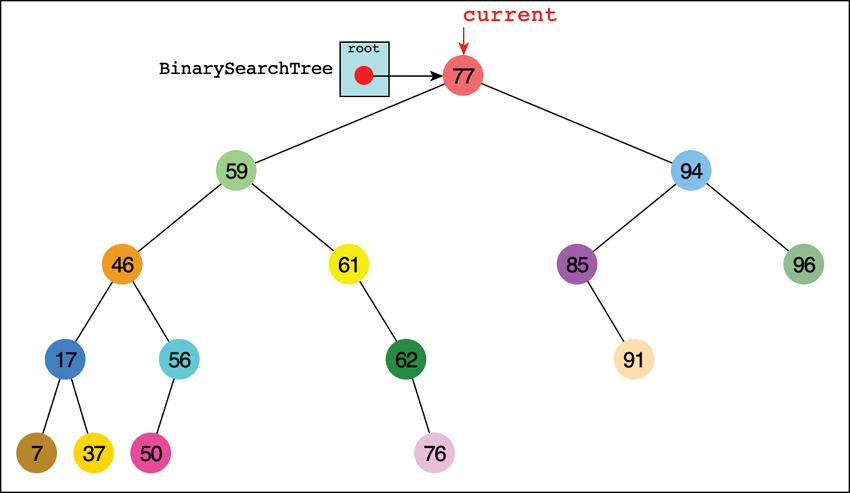
FIGURE 8-8 Finding the node with key 50
Enter the key value in the text entry box, hold down the Shift key, and select the Search button, and then the Step button,  . By repeatedly pressing the Step button, you can see all the individual steps taken to find key 50. On the second press, the current pointer shows up at the root of the tree, as seen in Figure 8-8. On the next click, a parent pointer shows up that will follow the current pointer. Ignore that pointer and the code display for a moment; we describe them in detail shortly.
. By repeatedly pressing the Step button, you can see all the individual steps taken to find key 50. On the second press, the current pointer shows up at the root of the tree, as seen in Figure 8-8. On the next click, a parent pointer shows up that will follow the current pointer. Ignore that pointer and the code display for a moment; we describe them in detail shortly.
As the Visualization tool looks for the specified node, it makes a decision at the current node. It compares the desired key with the one found at the current node. If it’s the same, it’s found the desired node and can quit. If not, it must decide where to look next.
In Figure 8-8 the current arrow starts at the root. The program compares the goal key value 50 with the value at the root, which is 77. The goal key is less, so the program knows the desired node must be on the left side of the tree—either the root’s left child or one of that child’s descendants. The left child of the root has the value 59, so the comparison of 50 and 59 will show that the desired node is in the left subtree of 59. The current arrow goes to 46, the root of that subtree. This time, 50 is greater than the 46 node, so it goes to the right, to node 56, as shown in Figure 8-9. A few steps later, comparing 50 with 56 leads the program to the left child. The comparison at that leaf node shows that 50 equals the node’s key value, so it has found the node we sought.
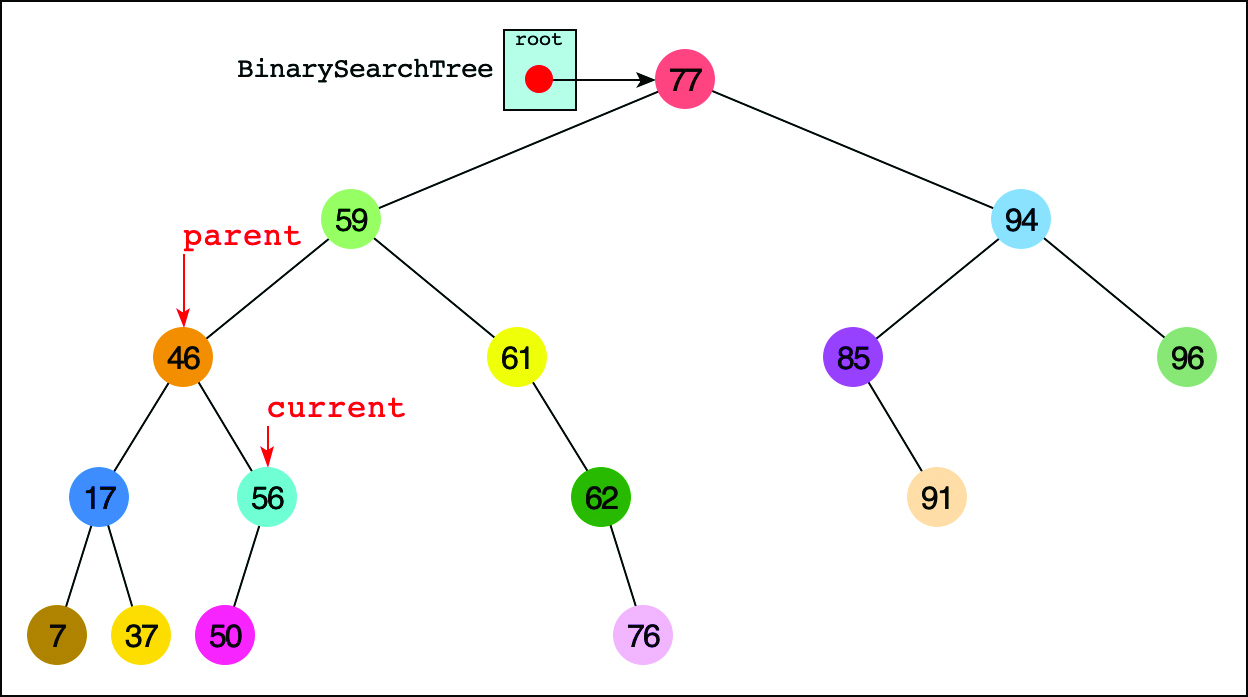
FIGURE 8-9 The second to last step in finding key 50
The Visualization tool changes a little after it finds the desired node. The current arrow changes into the node arrow (and parent changes into p). That’s because of the way variables are named in the code, which we show in the next section. The tool doesn’t do anything with the node after finding it, except to encircle it and display a message saying it has been found. A serious program would perform some operation on the found node, such as displaying its contents or changing one of its fields.
Python Code for Finding a Node
Listing 8-3 shows the code for the __find() and search() methods. The __find() method is private because it can return a node object. Callers of the BinarySearchTree class use the search() method to get the data stored in a node.
LISTING 8-3 The Methods to Find a Binary Search Tree Node Based on Its Key
class BinarySearchTree(object): # A binary search tree class
…
def __find(self, goal): # Find an internal node whose key
current = self.__root # matches goal and its parent. Start at
parent = self # root and track parent of current node
while (current and # While there is a tree left to explore
goal != current.key): # and current key isn't the goal
parent = current # Prepare to move one level down
current = ( # Advance current to left subtree when
current.leftChild if goal < current.key else # goal is
current.rightChild) # less than current key, else right
# If the loop ended on a node, it must have the goal key
return (current, parent) # Return the node or None and parent
def search(self, goal): # Public method to get data associated
node, p = self.__find(goal) # with a goal key. First, find node
return node.data if node else None # w/ goal & return any data
The only argument to __find() is goal, the key value to be found. This routine creates the variable current to hold the node currently being examined. The routine starts at the root – the only node it can access directly. That is, it sets current to the root. It also sets a parent variable to self, which is the tree object. In the Visualization tool, parent starts off pointing at the tree object. Because parent links are not stored in the nodes, the __find() method tracks the parent node of current so that it can return it to the caller along with the goal node. This capability will be very useful in other methods. The parent variable is always either the BinarySearchTree being searched or one of its __Node objects.
In the while loop, __find() first confirms that current is not None and references some existing node. If it doesn’t, the search has gone beyond a leaf node (or started with an empty tree), and the goal node isn’t in the tree. The second part of the while test compares the value to be found, goal, with the value of the current node’s key field. If the key matches, then the loop is done. If it doesn’t, then current needs to advance to the appropriate subtree. First, it updates parent to be the current node and then updates current. If goal is less than current’s key, current advances to its left child. If goal is greater than current’s key, current advances to its right child.
Can't Find the Node
If current becomes equal to None, you’ve reached the end of the line without finding the node you were looking for, so it can’t be in the tree. That could happen if the root node was None or if following the child links led to a node without a child (on the side where the goal key would go). Both the current node (None) and its parent are returned to the caller to indicate the result. In the Visualization tool, try entering a key that doesn’t appear in the tree and select Search. You then see the current pointer descend through the existing nodes and land on a spot where the key should be found but no node exists. Pointing to “empty space” indicates that the variable’s value is None.
Found the Node
If the condition of the while loop is not satisfied while current references some node in the tree, then the loop exits, and the current key must be the goal. That is, it has found the node being sought and current references it. It returns the node reference along with the parent reference so that the routine that called __find() can access any of the node’s (or its parent’s) data. Note that it returns the value of current for both success and failure of finding the key; it is None when the goal isn’t found.
The search() method calls the __find() method to set its node and parent (p) variables. That’s what you see in the Visualization tool after the __find() method returns. If a non-None reference was found, search() returns the data for that node. In this case, the method assumes that data items stored in the nodes can never be None; otherwise, the caller would not be able to distinguish them.
Tree Efficiency
As you can see, the time required to find a node depends on its depth in the tree, the number of levels below the root. If the tree is balanced, this is O(log N) time, or more specifically O(log2 N) time, the logarithm to base 2, where N is the number of nodes. It’s just like the binary search done in arrays where half the nodes were eliminated after each comparison. A fully balanced tree is the best case. In the worst case, the tree is completely unbalanced, like the examples shown in Figure 8-6, and the time required is O(N). We discuss the efficiency of __find() and other operations toward the end of this chapter.
