- 3.1 Evolving Network Requirements
- 3.2 The SDN Approach
- 3.3 SDN- and NFV-Related Standards
- 3.4 Key Terms
3.2 The SDN Approach
This section provides an overview of SDN and shows how it is designed to meet evolving network requirements.
Requirements
Based on the narrative of Section 3.1, we are now in a position to detail the principal requirements for a modern networking approach. The Open Data Center Alliance (ODCA) provides a useful, concise list of requirements, which include the following [ODCA14]:
- Adaptability: Networks must adjust and respond dynamically, based on application needs, business policy, and network conditions.
- Automation: Policy changes must be automatically propagated so that manual work and errors can be reduced.
- Maintainability. Introduction of new features and capabilities (software upgrades, patches) must be seamless with minimal disruption of operations.
- Model management: Network management software must allow management of the network at a model level, rather than implementing conceptual changes by reconfiguring individual network elements.
- Mobility: Control functionality must accommodate mobility, including mobile user devices and virtual servers.
- Integrated security: Network applications must integrate seamless security as a core service instead of as an add-on solution.
- On-demand scaling: Implementations must have the ability to scale up or scale down the network and its services to support on-demand requests.
SDN Architecture
An analogy can be drawn between the way in which computing evolved from closed, vertically integrated, proprietary systems into an open approach to computing and the evolution coming with SDN (see Figure 3.1). In the early decades of computing, vendors such as IBM and DEC provided a fully integrated product, with a proprietary processor hardware, unique assembly language, unique operating system (OS), and the bulk if not all of the application software. In this environment, customers, especially large customers, tended to be locked in to one vendor, dependent primarily on the applications offered by that vendor. Migration to another vendor’s hardware platform resulted in major upheaval at the application level.
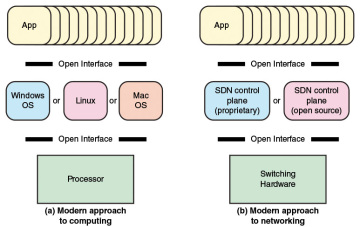
FIGURE 3.1 The Modern Approach to Computing and Networking
Today, the computing environment is characterized by extreme openness and great customer flexibility. The bulk of computing hardware consists of x86 and x86-compatible processors for standalone systems and ARM processors for embedded systems. This makes it easy to port operating systems implemented in C, C++, Java, and the like. Even proprietary hardware architectures, such as IBM’s zEnterprise line, provide standardized compilers and programming environments and so can easily run open sources operating systems such as Linux. Therefore, applications written for Linux or other open operating systems can easily be moved from one vendor platform to another. Even proprietary systems such as Windows and Mac OS provide programming environments to make porting of applications an easy matter. It also enables the development of virtual machines that can be moved from one server to another across hardware platforms and operating systems.
The networking environment today faces some of the same limitations faced in the pre-open era of computing. Here the issue is not developing applications that can run on multiple platforms. Rather, the difficulty is the lack of integration between applications and network infrastructure. As demonstrated in the preceding section, traditional network architectures are inadequate to meet the demands of the growing volume and variety of traffic.
The central concept behind SDN is to enable developers and network managers to have the same type of control over network equipment that they have had over x86 servers. As discussed in Section 2.6 in Chapter 2, the SDN approach splits the switching function between a data plane and a control plane that are on separate devices (see Figure 3.2). The data plane is simply responsible for forwarding packets, whereas the control plane provides the “intelligence” in designing routes, setting priority and routing policy parameters to meet QoS and QoE requirements and to cope with the shifting traffic patterns. Open interfaces are defined so that the switching hardware presents a uniform interface regardless of the details of internal implementation. Similarly, open interfaces are defined to enable networking applications to communicate with the SDN controllers.
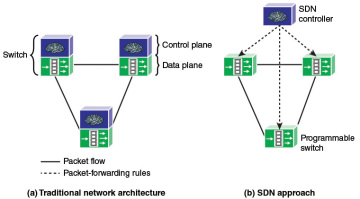
FIGURE 3.2 Control and Data Planes
 See Figure 2.15, Software Defined Networking
See Figure 2.15, Software Defined Networking
Figure 3.3 elaborates on the structure shown in Figure 2.15, showing more detail of the SDN approach. The data plane consists of physical switches and virtual switches. In both cases, the switches are responsible for forwarding packets. The internal implementation of buffers, priority parameters, and other data structures related to forwarding can be vendor dependent. However, each switch must implement a model, or abstraction, of packet forwarding that is uniform and open to the SDN controllers. This model is defined in terms of an open application programming interface (API) between the control plane and the data plane (southbound API). The most prominent example of such an open API is OpenFlow, discussed in Chapter 4, “SDN Data Plane and OpenFlow.” As Chapter 4 explains, the OpenFlow specification defines both a protocol between the control and data planes and an API by which the control plane can invoke the OpenFlow protocol.
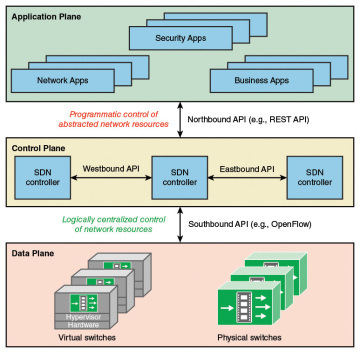
FIGURE 3.3 Software-Defined Architecture
SDN controllers can be implemented directly on a server or on a virtual server. OpenFlow or some other open API is used to control the switches in the data plane. In addition, controllers use information about capacity and demand obtained from the networking equipment through which the traffic flows. SDN controllers also expose northbound APIs, which allow developers and network managers to deploy a wide range of off-the-shelf and custom-built network applications, many of which were not feasible before the advent of SDN. As yet there is no standardized northbound API nor a consensus on an open northbound API. A number of vendors offer a REpresentational State Transfer (REST)-based API to provide a programmable interface to their SDN controller.
 See Chapter 5, “SDN Control Plane”
See Chapter 5, “SDN Control Plane”
Also envisioned but not yet defined are horizontal APIs (east/westbound), which would enable communication and cooperation among groups or federations of controllers to synchronize state for high availability.
At the application plane are a variety of applications that interact with SDN controllers. SDN applications are programs that may use an abstract view of the network for their decision-making goals. These applications convey their network requirements and desired network behavior to the SDN controller via a northbound API. Examples of applications are energy-efficient networking, security monitoring, access control, and network management.
Characteristics of Software-Defined Networking
Putting it all together, the key characteristics of SDN are as follows:
- The control plane is separated from the data plane. Data plane devices become simple packet-forwarding devices (refer back to Figure 3.2).
- The control plane is implemented in a centralized controller or set of coordinated centralized controllers. The SDN controller has a centralized view of the network or networks under its control. The controller is portable software that can run on commodity servers and is capable of programming the forwarding devices based on a centralized view of the network.
- Open interfaces are defined between the devices in the control plane (controllers) and those in the data plane.
- The network is programmable by applications running on top of the SDN controllers. The SDN controllers present an abstract view of network resources to the applications.
